Project Context
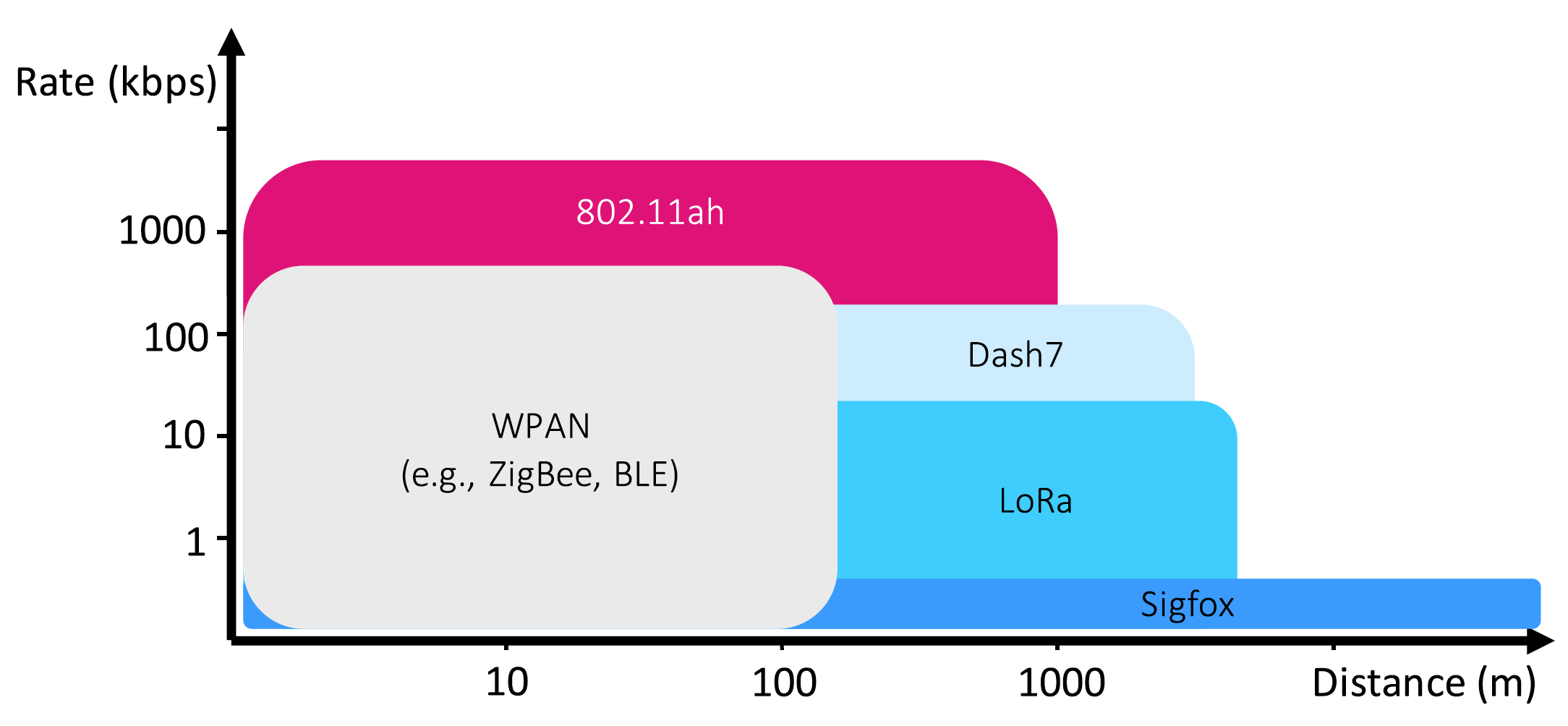
The IoT domain is characterized by many applications that require low-bandwidth communications over a long range, at a low cost and at low power. This has given rise to novel ‘SIM-less’ radio technologies that try to fill in this existing market gap of low-power wide area IoT networks, often referred to as Low Power Wide Area Networks or LPWANs. Due to the use of sub-GHz radio frequencies (typically 433 or 868 MHz), a single LPWAN base station has a large coverage area, with typical transmission ranges in the order of 1 up to 50 kilometers. As a result, a single base station can support high numbers of connected devices (> 1000 per base station).
Notorious initiatives in this domain are LoRa and Sigfox. They aim to create a network of base stations, so that only the sensors need to be deployed. Although these standards have similar goals, they are very different in terms of technology (e.g., wideband vs ultra narrow band), operation mode (multiple versus single operator) and whether or not a company is allowed to install their own gateways. These are however not the only technologies being introduced. Very recently, the IEEE 802.11 family has been extended with a LPWAN solution, IEEE 802.11ah (or “HaLow”). Like existing Wi-Fi, 802.11ah provides IP-based connectivity, allowing devices to communicate with a broad range of hardware platforms. As such, this technology is a prime candidate for inclusion in future residential and industrial access points. This standard offers many configuration options and a wide range of supported bandwidths, making it more versatile than existing LPWAN solutions, but introducing more challenges regarding management and configuration at multiple levels of the protocol stack. Finally, to further complicate the technology choice for companies, other technologies such as Dash7, Weightless and IEEE 802.15.4g utilize the same radio frequencies, thereby competing (and possibly interfering) with other LPWAN technologies.
Although these new technologies have the potential to significantly impact many IoT deployments, many uncertainties and challenges exist related to deployment, management and coexistence aspects, making adoption of these technologies difficult for many Flemish companies.
Project Goals
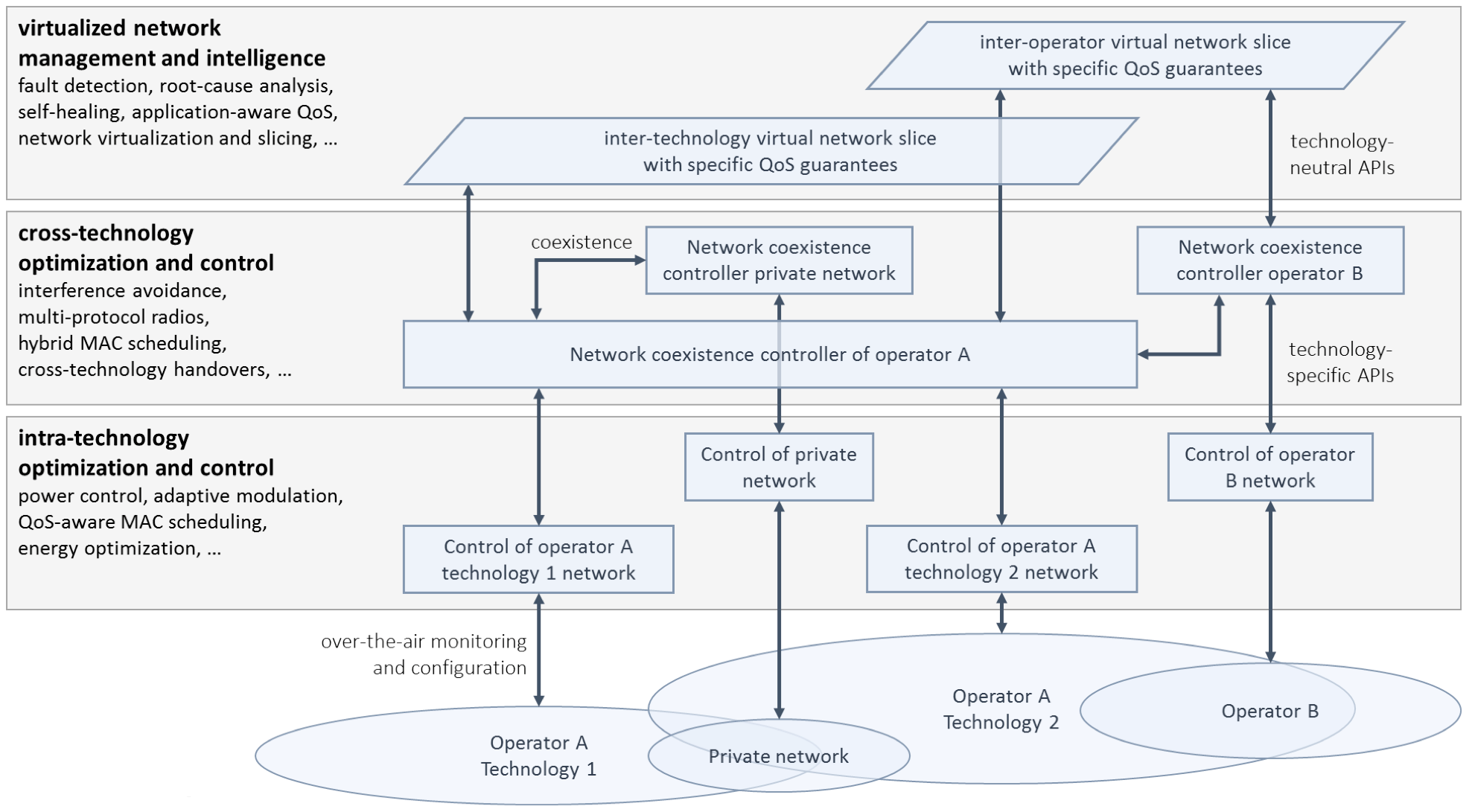
This SBO project will investigate management & optimization challenges related to LPWAN technologies and develop related novel solutions related to the following topics.
- Technology insights
- Single-technology performance evaluation of the suitability of different LPWAN technologies for different application domain in terms of coverage, reliability, throughput, QoS, scalability, localization accuracy, mobility support, etc.
- Emerging end-to-end IoT protocol performance. Evaluation of the performance and interactions of different LPWAN technologies with existing and emerging IoT standards and protocols, such as 6LoWPAN (with UDP or TCP) and RPL.
- Interference analysis. Analysis of the mutual interference of sub-1Ghz LPWAN technologies.
- Techno-economical studies. Co-analysis of both technical and financial aspects for deployment and utilization of new LPWAN technologies, encompassing capital and operational expenditures.
- Real-time control, reconfiguration and optimization
- Co-existence improvements. Development of both coordinated and distributed coexistence-improving algorithms and solutions to minimize interference among coexisting LPWAN networks.
- Scalability improvements. Improvements of LPWAN technologies in terms of device density (number of connected devices).
- Mobility and handover management: Development of strategies, algorithms and protocols for extending the current point to multipoint model to a fully-networked solution including support for handovers, meshing, etc.
- Differentiated QoS support. Analysis of optimal configuration options for LPWAN technologies for supporting applications that have (real-time) QoS requirements.
- Management of networks & services
- Indoor and outdoor localization. Development & analysis of localization algorithms based on LPWAN technologies.
- Diagnostics & monitoring. Local, distributed and centralized monitoring solutions for automated troubleshooting of LPWAN networks, including fault detection and root cause analysis.
- Scalable network management strategies. Development of strategies, protocols, algorithms and techniques for automatically managing, configuring & maintaining 1000+ devices with different application QoS requirements.
- Multi-provider optimizations. Negotiation strategies and algorithms for switching between networks managed by different providers, including handover strategies.
- Network virtualization & software defined networking. Efficient network management strategies for networks with multiple stakeholders, e.g. through the outsourcing of the network management to third parties.
- Deployment & network planning strategies. Tools and strategies for deciding optimal locations and conditions for deploying new LPWAN gateways, including the development deterministic path loss models to accurately predict network coverage.




